This blog post is aimed to provide a quick reference for the list of design considerations for architecting and implementing VMware on AWS.
The post is divided into two sections. First section lists the key design considerations in a tabular format and the second one will have more details on the features/considerations.
List of key design considerations / features
Design Consideration | Details | ||||||||||||
Subscription | The Subscription model is similar to an AWS Regional Reserved Instance. Subscriptions are fixed on the following attributes: AWS Region VMware Cloud Org Host instance type | ||||||||||||
Shared Responsibility | Customers should understand the shared responsibility model. VMWare is responsible for the lifecycle of vSphere, VSAN and NSX. Customers are responsible for configuration of VMs, networks and applications they manage. | ||||||||||||
Cloud Services Console | VMware Cloud Services Console provides UI to manage
| ||||||||||||
AWS Accounts |
| ||||||||||||
Management Subnet | When deploying SDDC, customers must provide a number of hosts and management ip range.
A VPC is created in VMWare managed aws account using the SDDC management IP address range provided during the deployment process, with several additional subnets also created within that VPC at the same time. | ||||||||||||
Connected VPC | Any services utilized in the customer account of connected VPC are paid by the customer | ||||||||||||
Host Types | i3 (36 cores, 512GiB RAM, and 10.37TiB raw storage). Suitable for:
i3en (96 cores, 768 GiB RAM and 45.84TB raw storage). Suitable for:
Cluster conversion from i3 to i3en can be done by contacting VMware. | ||||||||||||
Cluster | Types:
Once a cluster increases to 3 or more, the cluster cannot be shrunk to 1 or 2. Allowed transformations:
| ||||||||||||
Stretched Cluster | Does not protect against regional level failures. Add or remove hosts are done in pairs, one in each AZ. Max hosts per cluster is the same as a standard cluster (16). Minimum hosts supported for a stretched cluster is 2. Once a stretched cluster increases to 6 or more, the cluster cannot be shrunk to 2 or 4 hosts. | ||||||||||||
Base / Primary Cluster (Cluster-1) | Base cluster, the first cluster deployed in a SDDC, hosts management appliances and NSX edges. Datastores created in a base cluster:
Resource pools created in a base cluster:
| ||||||||||||
Additional Clusters | Logical networks created in SDDC are automatically shared across all clusters. They contain only workloadDatastores | ||||||||||||
Custom Cluster | Specify just the number of CPU cores you need per host. Reduces costs for running applications licensed per-core. Changing the number of cores does not affect the price of the host. | ||||||||||||
Number of clusters | Large clusters vs Small clusters:
Island clusters:
| ||||||||||||
Elastic DRS | Elastic DRS automatically adds or removes hosts from a cluster in response to utilization of cpu, ram and storage. eDRS algorithm runs every 5 mins. Configured at cluster level (in vcenter). Elastic DRS baseline policy is always running and cannot be disabled | ||||||||||||
Elastic DRS Thresholds | |||||||||||||
Resource Pools | All workloads should be placed within Compute-ResourcePool. It is possible to create workloads outside of Compute-ResourcePool. However, it is strongly discouraged due to the potential for creating resource contention between workloads which exist within Resource Pools and those that do not | ||||||||||||
Management appliance sizes | Supported sizes medium and large. By default, a new SDDC is created with medium-sized NSX Edge and vCenter Server appliances. Large-sized appliances are recommended for deployments with more than 30 hosts or 3000 VMs | ||||||||||||
Storage options | Directly attached storage using VSAN AWS Storage Services
Managed Services Provider Storage
APN Storage partners | ||||||||||||
VSAN Logical Datastores | vSAN has been modified to present two logical Datastores from the same underlying physical storage.
Separation exists purely as a means of enforcing permissions on the storage for management appliances The free space, used space, and total capacity numbers will be identical between the two logical Datastores, because both reflect the same underlying pool of capacity. | ||||||||||||
VSAN Slack space | VSAN requires slack space for operations such as deduplication, object re-balancing, and for recovering from hardware outages. Since November 2021 the slack space required is 20%, earlier it was 30%. To enforce the slack space requirement eDRS will automatically scale up SDDC if storage consumption crosses 79%. | ||||||||||||
VSAN Storage policies | |||||||||||||
VSAN Encryption | |||||||||||||
Interconnectivity options | VPN DX VTGW HCX | ||||||||||||
SDDC – DX Connectivity | Can connect to Direct Connect DX. Both private VIF and public VIF are supported. Cannot be directly connected to DXGW. Use the SDDC group to connect DXGW through VTGW. | ||||||||||||
SDDC Group | A SDDC group can only have SDDC members in the same region. | ||||||||||||
VTGW | Attachments
Provides below connectivity
Doesn’t allow native VPC to native VPC communication. One Direct Connect VIF for on-prem connectivity to all SDDCs in the same group. | ||||||||||||
VSAN Policy | |||||||||||||
Compute Policies | |||||||||||||
Additional Bandwidth ( for N-S traffic ) | In default configurations SDDC network has a single T-0 router (VMXNET3 NIC) Additional T-0 routers can be created by creating traffic groups. Requirements for traffic groups – Must connect SDDC to VTGW , by creating a SDDC Group. – SDDCs should have large-size management appliances and at least four hosts NIC Bandwidths – vmxnet3 10gbps – TGW attachment 50gbps | ||||||||||||
Default Route | SDDC is configured with a default route which points to its upstream Internet Gateway (IGW) | ||||||||||||
Policy based VPN | when new routes are added, the routing tables must be updated on both ends of the network Appropriate choice if – On-prem VPN does not support BGP – Only a few networks on either ends of VPN. | ||||||||||||
Layer 2 extension | Two ways to extend a network from on-prem. – Layer-2 VPN Tunnel using NSX Autonomous edge appliance – HCX network extension | ||||||||||||
BGP route filtering on VMC side | |||||||||||||
IP Addresses | |||||||||||||
Subnet for ENIs in Connected VPC | – Recommended subnet size | ||||||||||||
Management Subnet | |||||||||||||
Connected VPC | – | ||||||||||||
DHCP |
| ||||||||||||
DNS Forwarders in VMC |
| ||||||||||||
Conditional Forwarding | How does conditional forwarding work? When a DNS query is received, the DNS forwarder compares the domain name in the query with the domain names in the FQDN DNS zones.
Zone Types
Each zone contains the following details
Source IP:
| ||||||||||||
VMC DNS Gotcha |
| ||||||||||||
DNS Forwarder | NSX-T Tier 1 Gateways (MGW and CGW) only act as forwarders, relaying the queries from VMs to the actual DNS servers specified. – Onprem DNS Servers – Local DNS Servers – Customer managed DNS on EC2 – AWS managed DNS using AWS Directory services – Route53 resolver inbound endpoint Don’t use Amazon’s provided DNS a.k.a .2 dns resolver. It has a limit of 1,024 queries per second from an endpoint, and in the case of VMC the limit is shared with all the VMs running within the SDDC. | ||||||||||||
Route 53 |
| ||||||||||||
Route 53 Resolver |
| ||||||||||||
Route 53 Resolver DNS Firewall | The following traffic is filtered by the firewall.
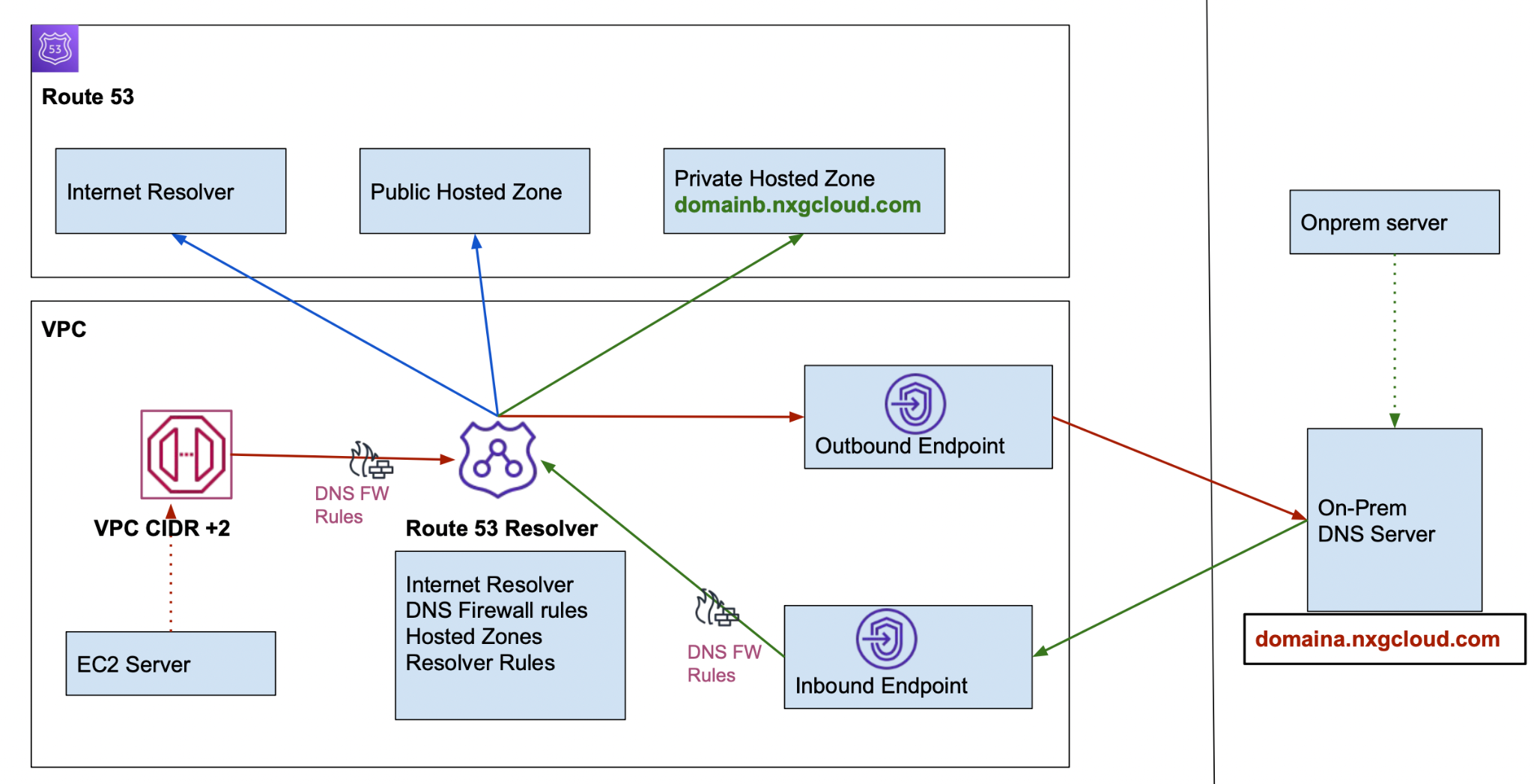 | ||||||||||||
DNS Forwarders in windows DNS Servers |
| ||||||||||||
Public IPs | Options – Use public IPs provided by VMC – BYOIP To use the IPs provided by VMC, you can request them in the VMC console and configure NAT. For BYOIP, NLBs have to be used. | ||||||||||||
BYOIPs | – In the Single SDDC environments, bring IPs to aws account which has connected VPC and assign the IPs to NLBs that have VMC vms as targets. – In multiregion environments , create NLBs in custom VPCs and attach the VPCs to VTGW. Reference architecture here | ||||||||||||
Backup | |||||||||||||
Disaster Recovery | |||||||||||||
Upgrades and Maintenance | VMware sends a notification email, 7 days before a regular update and 2 days before an emergency update During upgrades the following operations fail – Provisioning new vm – Hot or Cold migrations | ||||||||||||
Add Ons | HCX is provided free to all SDDCs. Log Insight trial version is enabled by default. vRA Carbon black NSX Advanced firewall | ||||||||||||
Monitoring SDDC traffic | VMC supports IPFIX and port mirroring. | ||||||||||||
Hybrid linked mode | Every cloud SDDC has a dedicated vCenter instance that can, if required, be linked to an on-premises vCenter instance using the Hybrid Linked Mode (HLM) feature | ||||||||||||
Additional roles in vcenter | CloudAdmin CloudGlobalAdmin | ||||||||||||
Integration with native aws services | RDS ALB Monitoring
| ||||||||||||
Windows licensing | |||||||||||||
SQL server licensing | Models
| ||||||||||||
vCenter Inventory |
| ||||||||||||
vCenter Permissions |
| ||||||||||||
VMWare AWS Account | Whenever a new cloud services Organization (Org) is created, VMware creates a sub-account within this master account which acts as the parent for all AWS resources used by that Org. | ||||||||||||
SDDC Underlay VPC |
| ||||||||||||
ESXi Networking |
| ||||||||||||
VPC Cross-Link | Cross-Account ENIs are used to create a connection between every host within the base Cluster of the SDDC to a subnet within the cross-linked VPC. The cross-link provides the SDDC with a network forwarding path to services maintained within the customer-owned AWS account The Availability Zone (AZ) of the cross-link subnet will be used to determine the AZ placement of the hosts. | ||||||||||||
VSAN Encryption | VSAN Encryption is enabled by default on each cluster deployed in your SDDC, and can’t be turned off. vSAN uses AWS KMS to generate a Customer Master Key (CMK). CMK is used to generate KEK. KEK is used to encrypt DEKs generated for each disk.
| ||||||||||||
Uplinks of tier-0 edge router |
| ||||||||||||
Windows and SQL License | |||||||||||||
Logging |
|
Additional details for the above points
Stretched Cluster
Reference: https://vmc.techzone.vmware.com/vmc-arch/docs/compute/vmc-aws-stretched-cluster#section1
Shared Responsibility Model
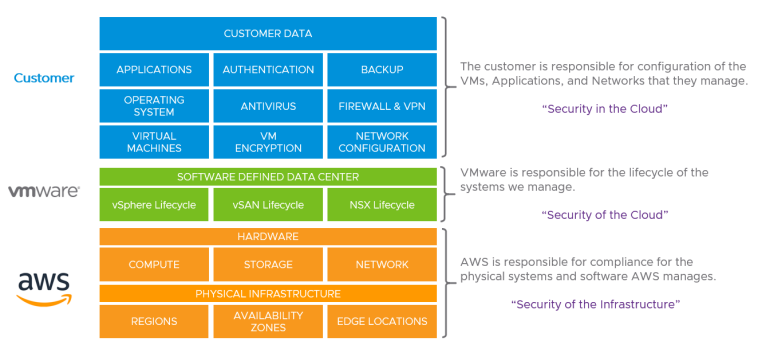
Source: https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-Cloud-on-AWS/solutions/VMware-Cloud-on-AWS.39646badb412ba21bd6770ef62ae00a2/GUID-31CC90E5EB22075B2313FA674D567F2A.html
VMWare Cloud Organization
Direct Connection
SDDC to DX over public VIF
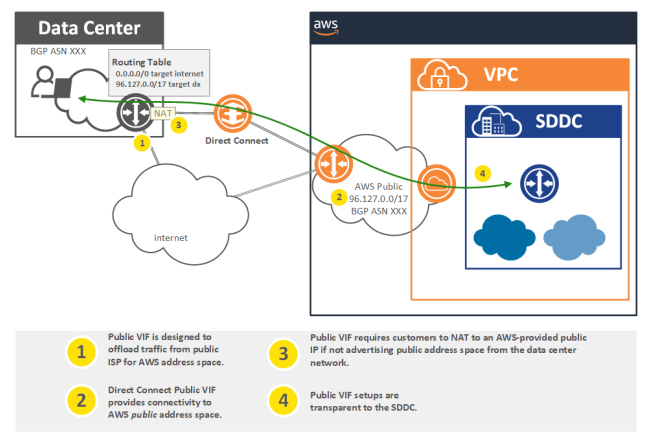
SDDC to DX over private VIF
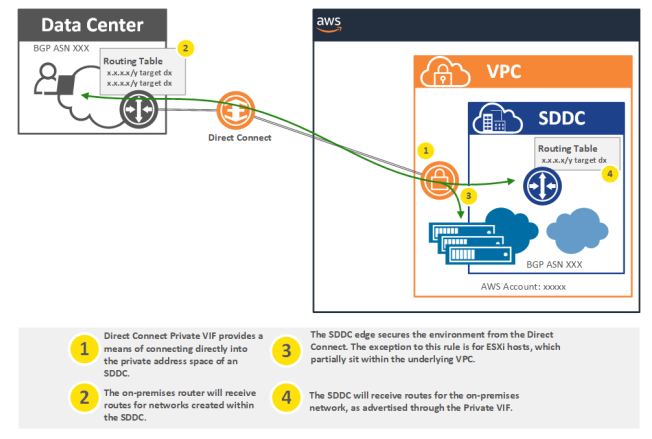
Source: https://vmc.techzone.vmware.com/vmc-arch/docs/network/vmc-aws-direct-connect#section2
SDDC Group
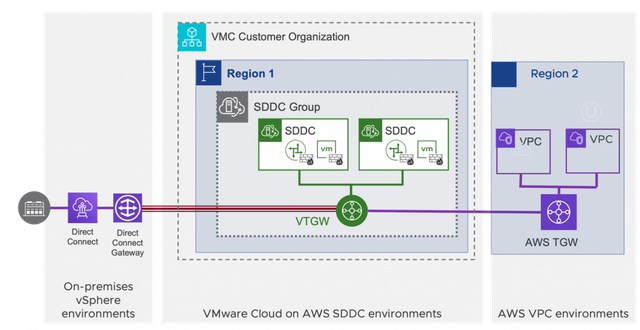
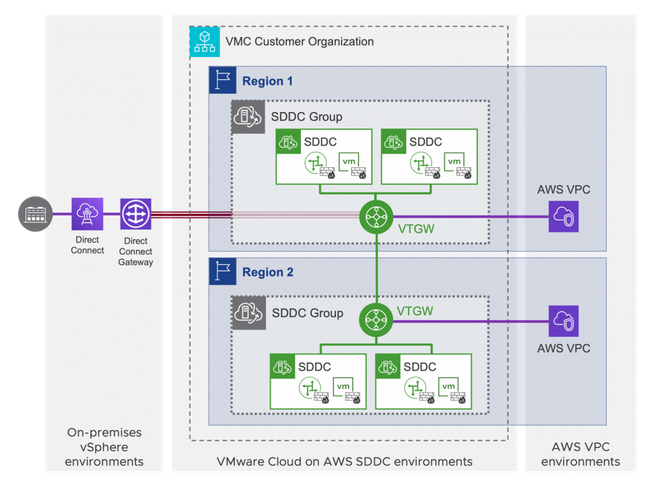
Multi-Edge SDDC
DNS Servers
https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-Cloud-on-AWS/solutions/GUID-25B7F9346825C50F67BF60403CCCAE21.html
https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/apn/choosing-the-right-dns-architecture-for-vmware-cloud-on-aws/
Elastic DRS
https://blogs.vmware.com/cloud/2019/05/15/elastic-drs-vmware-cloud-aws/
References
- VMWare Office Hours – Youtube
- VMWare AWS operations guide – here
- Vmc techzone sddc design – here
- Custom Cluster – VMWare blog
- Cluster types and sizes – vmctechzone
- Elastic DRS – vmctechzone
- Cluster design – vmware vmware
- SQL server licensing – vmware blog
- Very important links – vmc-aws-design-guide , vmc-aws-arch-guide
- https://vmc.techzone.vmware.com/vmc-solutions/activities/vmc-aws-design-guide#architectural-planning
- VMWare Cloud: Solution Design
- VMWare Cloud on AWS: SDDC Design
- https://vmc.techzone.vmware.com/vmc-arch/activities/vmc-aws-arch-guide#introduction
- https://vmc.techzone.vmware.com/vmc-solutions/activities/vmc-aws-design-guide#architectural-planning
- vSphere Sizing
- https://www.vmware.com/content/dam/digitalmarketing/vmware/en/pdf/certification/vmw-cimcasestudy-vspheresecurity-0.99.pdf

