Design Considerations
HCX Migration Types
Migration Type | Down time? | Concurrent Migration? | Short Description | Edition |
HCX vMotion | No | 1 / S.Mesh |
| Advanced |
Cold Migration | Yes | 1 / S.Mesh |
| Advanced |
Bulk Migration | Minimal | 250 / Mgr |
| Advanced |
Replication Assisted migration. | No | 200 / Mgr |
| Enterprise |
OS Assisted Migration | Yes | 50 disks / S.Mesh |
| Enterprise |
License
Activation Key | In private to public cloud deployment, activation keys come from public cloud providers. |
HCX Edition | HCX for VMware Cloud on AWS |
Service Mesh
Compute Profile | Compute profile captures the following information
|
Compute profile on Cloud HCX | On activating HCX on VMC, a compute profile is created automatically. We can login to HCX on the VMC side with cloudadmin@vmc.local user account and check the compute profile |
Uplink Network profiles on Cloud HCX | Uplink network profiles define how the migration traffic and network extension traffic flows between HCX appliances Onprem and VMC. HCX Interconnect and network extension appliances communicate over the internet or directconnect. These appliances create their own ipsec tunnels; they do not use the VPNs created in the VMC console . However, HCX managers can communicate over the VPN tunnels. On the VMC side, the following network profiles are created by default
|
Configure HCX to use Direct Connect |
Reference: Link1 |
Mobility Optimized Networking ( enterprise edition feature) | Solves hairpinning or tromboning effect for migrated VMs i.e. Avoids a long round trip network path via on-prem gateway The network path of routed traffic for migrated VMs
Reference: vmw-doc |
Traffic Engineering ( enterprise edition feature) |
Reference: vmw-blog vmw-bp-doc license-doc vmw-blog |
Mobility Groups |
HCX Concepts
HCX Components
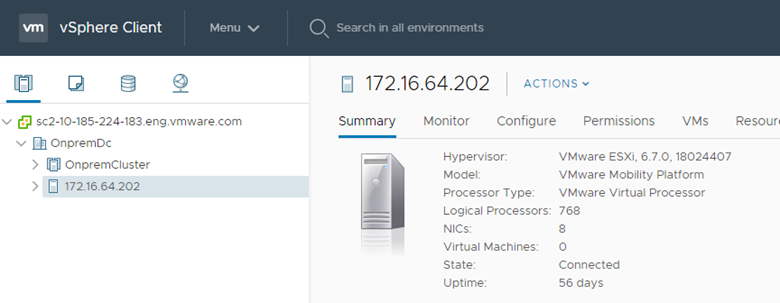
What is a Proxy Host?
It is a two-way vmotion proxy.
- When a vMotion is initiated to a remote host, the local ESXi host migrates that VM to the local proxy ESXi host.
- HCX-IX appliance transfers the VM data to remote HCX-IX appliance.
- Target proxy ESXi host migrates the VM to target ESXi host
How to deploy the Proxy host?
When a service mesh is created with “vMotion Migration Service” selected, a proxy host gets automatically deployed on vCenter. It’s purpose is
- It looks like nested ESXi, but it isn’t. It is a dedicated mobility platform.
- The processor, memory, storage and networking resources displayed on this object does not represent actual consumption on the physical hypervisor hosting the IX appliance.
References:
- https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-HCX/4.3/hcx-user-guide/GUID-9D3270E2-E7B1-42E6-A385-E5207957FCDB.html
- https://www.softwaredefinedblog.com/hcx/hcx-mobility-agent-aka-dummy-host/
HCX Appliances
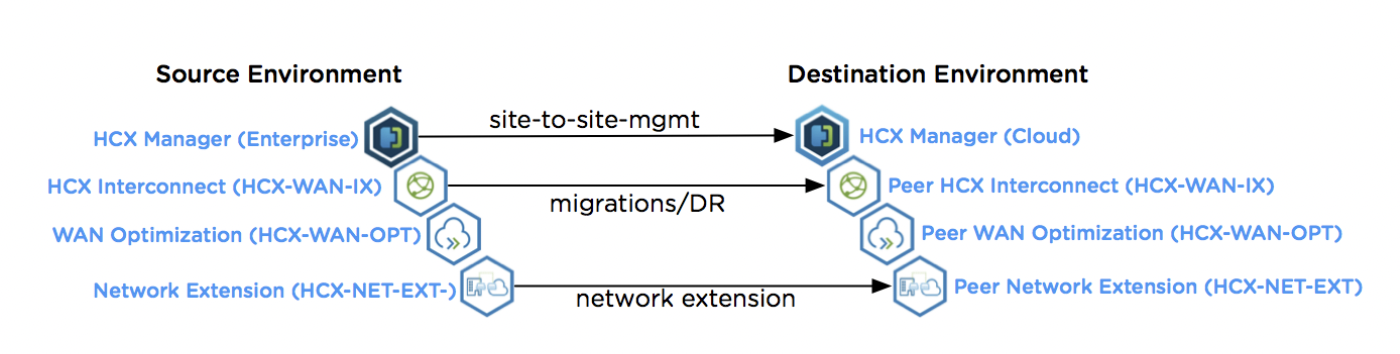
Appliance | Services |
Interconnect (HCX-IX) | 1. Replication based migration 2. vMotion based migration 3. Deploys Mobility Agent service that appears as a host object in the vCenter server. |
WAN Optimization (HCX-WO) | 1. Applies WAN optimization techniques like the data de-duplication and line conditioning. 2. It accelerates on-boarding to the destination site using Internet connections, without waiting for Direct Connect/MPLS circuits. |
Network Extension (HCX-NE) | Layer 2 Extension |
Sentinel Gateway | Connects and forwards source workloads to destination ( In OS assisted migrations ) |
Sentinel Data Receiver | Receive, manage, and monitor data replication operations at the destination environment ( In OS assisted migrations ) |
HCX Traffic Types
Management | HCX appliances use the network to communicate with HCX Manager, vCenter Server, NTP, DNS. |
Uplink | Local HCX appliances use the network to connect with remote HCX appliances and vice versa. |
vMotion | HCX appliances use the network to communicate with the vMotion interface of ESXi hosts. |
vSphere Replication | HCX appliances use the network to communicate with the vSphere replication interface of ESXi hosts. To reach the vSphere replication interface of ESXi hosts. |
HCX Guest Network | To connect to the Sentinel agents. |
HCX Installation Flow
VMC | Deploy HCX on VMC | |
VMC | Download HCX OVA for On-Prem | |
On-prem | Deploy OVA | |
On-prem | Activate and Register HCX | |
On-prem | Register vCenter. Register NSX (optional) | |
On-prem | Restart Services | |
On-Prem | Pair Sites | |
On-Prem | Create network profiles | |
On-Prem | Create compute profile | |
On-Prem | Create Service Mesh |
References
- https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-HCX/4.1/hcx-user-guide/GUID-C4CC758B-CAA4-42B9-92C3-9F16D10E25C5.html
- https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-HCX/4.2/hcx-getting-started/GUID-AB56D9A9-7E2C-436F-9E20-445E447E300F.html

